Bioavailability Breakthrough: Water-Soluble Cannabis Technologies Explained
Introduction
As cannabis consumption evolves, so does the technology behind making cannabinoids more bioavailable. Traditionally, cannabis has been consumed through smoking, vaporization, or edibles infused with oil-based cannabinoids. However, one of the biggest challenges with cannabis-infused products is bioavailability—how efficiently the body absorbs and utilizes cannabinoids like THC and CBD.
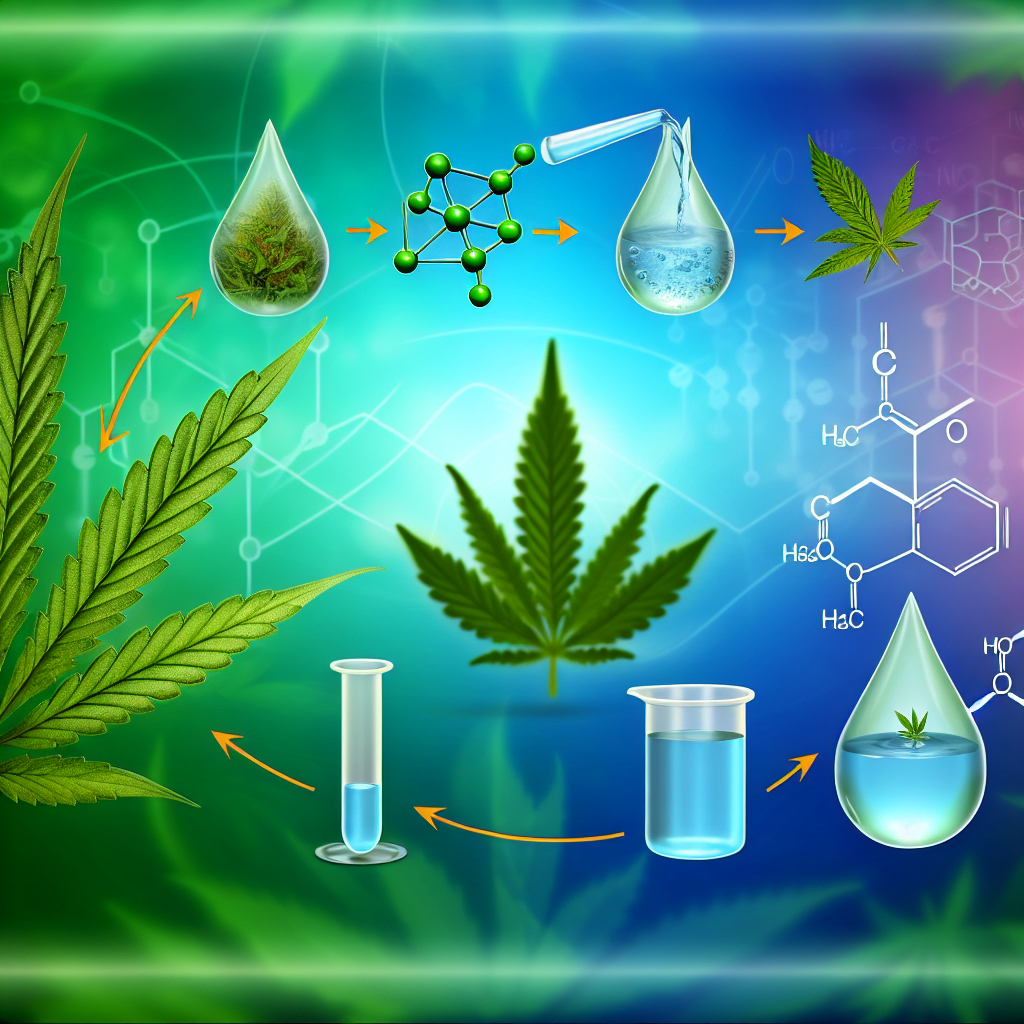
Water-soluble cannabis technologies have emerged as a game-changer, allowing cannabinoids to dissolve in water, dramatically improving their absorption into the bloodstream while ensuring faster onset times and enhanced effect predictability. This breakthrough revolutionizes product variety, enabling companies to create water-based beverages, sublingual sprays, and powdered cannabis formulations that dissolve seamlessly in liquids.
The Science Behind Water-Soluble Cannabis: How It Works
Nanoemulsions: Unlocking Maximum Absorption
Nanoemulsification breaks cannabis oil into microscopic droplets, allowing it to mix with water more efficiently. This dramatically increases bioavailability by making it easier for the body to absorb cannabinoids through mucous membranes and the digestive tract.
Microencapsulation: Stability and Longevity
Microencapsulation involves encasing cannabinoids in a protective nano-sized shell, improving their stability and solubility. This process shields cannabinoids from degradation due to light, heat, and oxidation, ensuring longer shelf life and effectiveness.
Why Water-Soluble Cannabis Is More Effective
Faster Onset Time
With traditional edibles, cannabis is first metabolized in the liver, delaying effects by up to two hours. In contrast, water-soluble cannabinoids are absorbed within 30 minutes to one hour, making the effects far more predictable.
Increased Absorption and Efficacy
Because traditional oil-based cannabis products have low bioavailability (4-12%), a large portion of the consumed THC or CBD is lost. Water-soluble cannabis bypasses many of the digestive system’s barriers, leading to more cannabinoids reaching the bloodstream.
Improved Dosing Accuracy
Unlike oil-based edibles, which may produce unpredictable effects, water-soluble cannabis provides consistent and controlled absorption, reducing the likelihood of overconsumption.
Medical and Therapeutic Benefits of Water-Soluble Cannabis
Beyond recreational use, water-soluble cannabinoids have significant medical potential. Their higher absorption rate and stability make them promising for conditions requiring rapid relief and precise dosing.
The Future of Cannabis: Exploring New Product Innovations
Water-soluble cannabis enables businesses and consumers to explore a new generation of cannabis-infused products, such as cannabis-infused beverages, pharmaceutical-grade cannabis, sublingual drops & sprays, and powdered cannabis additives.
Conclusion: The Revolutionary Potential of Water-Soluble Cannabis
Water-soluble cannabis technologies are transforming the future of cannabinoid consumption, offering significantly improved bioavailability, rapid onset, and better control over effects. As scientific research continues to validate the benefits of water-soluble cannabis, the industry is set to embrace more efficient, fast-acting, and versatile cannabis products.
Summary:
Water-soluble cannabis technologies are revolutionizing the cannabis industry by dramatically improving the bioavailability, onset time, and dosing accuracy of cannabinoids. These advancements, enabled by nanoemulsion and microencapsulation techniques, allow for the creation of innovative water-based cannabis products like beverages, sprays, and powders that offer superior absorption and therapeutic potential compared to traditional oil-based formats.
References:
[Luo et al., 2020] – Nanoemulsion-Based Delivery (Molecules)
[Millar et al., 2022] – Pharmacokinetics of THC Beverages (Scientific Reports)
[Cherniakov et al., 2021] – Microencapsulation of Cannabinoids (Journal of Drug Delivery Science)
[Eisenberg et al., 2021] – Cannabinoids in Medical Treatment (Frontiers in Pharmacology)