Endocannabinoid System: Unlocking the Power of Medical Cannabis
Introduction
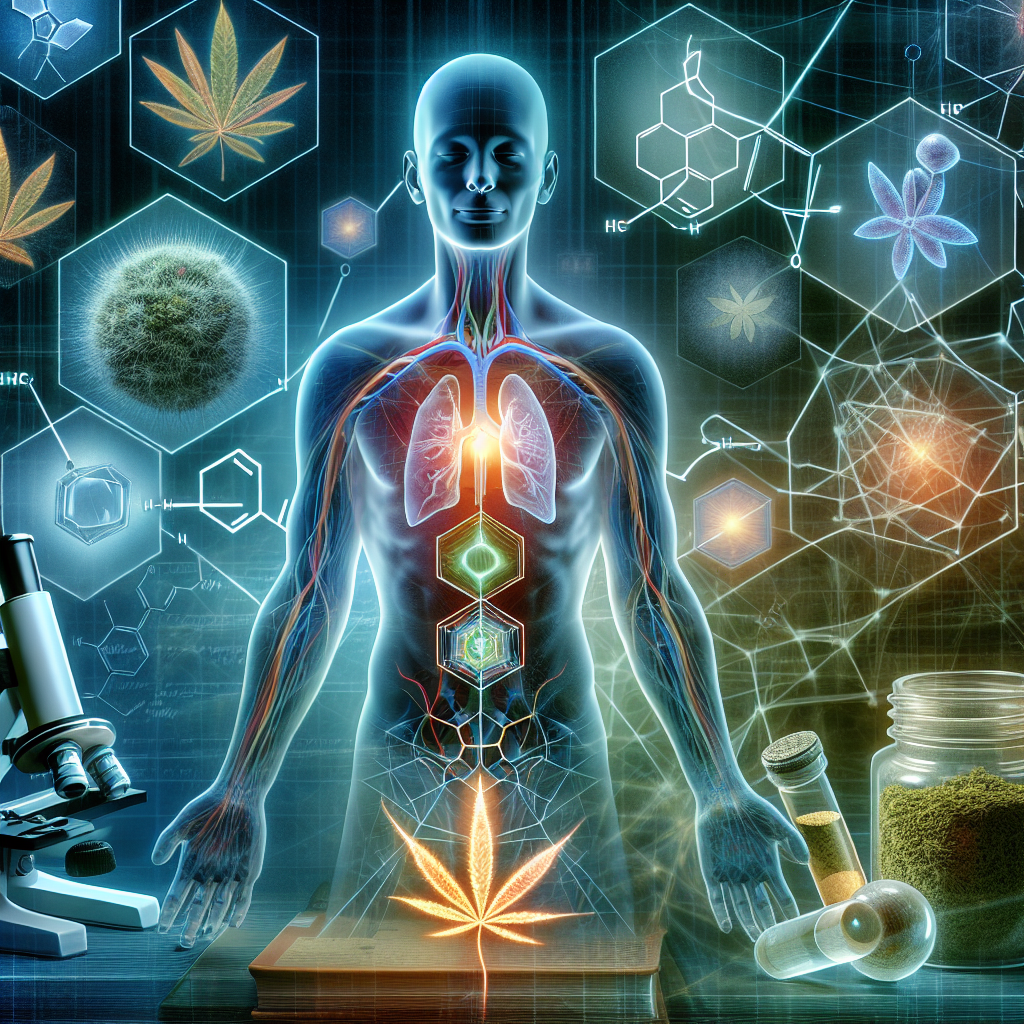
The therapeutic potential of medical cannabis lies within a groundbreaking biological network called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This vital system, discovered in the late 20th century, plays a central role in maintaining balance and homeostasis within the human body. Cannabis has a long history of medicinal use, and understanding its interaction with the ECS offers profound insights into how it can treat a wide range of conditions, from chronic pain to neurodegenerative diseases.
The Science Behind the ECS and Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis operates by modulating the activity of the ECS. Phytocannabinoids from cannabis interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors—THC primarily binds directly to CB1, while CBD has a more indirect approach to both receptors. These interactions influence a variety of health processes, showcasing cannabis’s therapeutic scope.
Targeting Inflammation: A New Frontier
One of the most exciting findings about medical cannabis is its potential to reduce inflammation through CB2 receptor interaction. This breakthrough positions cannabis as a viable option for treating chronic inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Chronic Pain and Spasticity: How THC and CBD Help
Chronic pain management is perhaps the most well-known application of medical cannabis. THC’s ability to bind to CB1 receptors in the brain has shown efficacy in reducing neuropathic and inflammatory pain.
Neuroprotection and Cognitive Health: Cannabis’s Role in Brain Function
Cannabis may also provide long-term neuroprotective effects. These findings open doors to addressing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease, where options have historically been limited.
Relieving Anxiety and Depression with the ECS
The ECS plays a vital role in psychological well-being through the regulation of neurotransmitters like anandamide. CBD is a promising option for individuals seeking relief from mental health issues without impairing daily function.
Exploring Cannabis’s Potential in Cancer Therapy
Medical cannabis has shown potential as an adjunct in cancer therapy. This ability to selectively target cancer cells opens exciting possibilities for using cannabis in oncology.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Although medical cannabis holds immense promise, challenges like restrictive federal policies and limited clinical trials hinder its wider application. However, as legalization progresses globally, the scientific focus on cannabis-ECS interactions is gaining momentum.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system serves as the backbone for many essential biological processes, and its relationship with medical cannabis is transforming modern healthcare. The interplay between endocannabinoids, CB1 and CB2 receptors, and phytocannabinoids like THC and CBD offers a robust framework for treating a wide range of conditions.
Concise Summary:
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a groundbreaking biological network that plays a central role in maintaining balance and homeostasis within the human body. Medical cannabis interacts with the ECS, offering promising solutions for various health conditions, including chronic pain, inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, and mental health challenges. While research in this field is still evolving, the therapeutic potential of the ECS and medical cannabis is transforming modern healthcare.
References:
[Journal of Clinical Investigation](https://www.jci.org/)
[The Lancet Neurology](https://www.thelancet.com/)
[Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease](https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-alzheimers-disease/jad160726)
[Frontiers in Psychiatry](https://www.frontiersin.org/)
[Oncotarget](https://oncotarget.com/)