Cannabinoid Interactions with Sodium Channels: Mechanisms Underlying Analgesic Effects for Neuropathic Pain
Introduction
In recent years, the exploration of **cannabinoids** for medical use has garnered significant attention, particularly their potential **analgesic effects** for conditions like **neuropathic pain**. Neuropathic pain, a chronic condition resulting from damage or dysfunction in the nervous system, is often characterized by shooting, burning pain or a sensitivity to touch. Traditional treatments, including **opioids** and **anticonvulsants**, often lack efficacy or come with adverse side effects, leading researchers to consider alternative therapies. One promising area of research is the interaction between cannabinoids and **sodium channels**, which may hold the key to unlocking safer and more effective pain relief mechanisms.
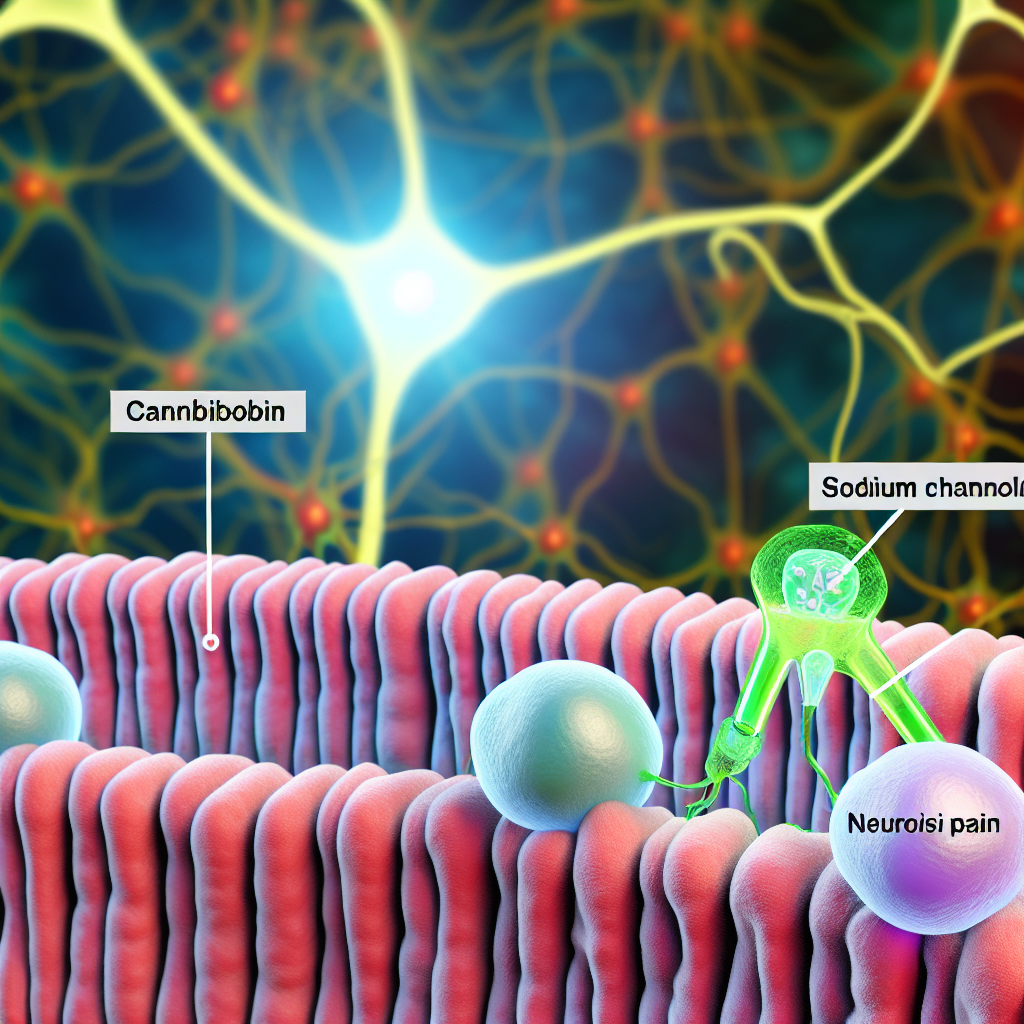
Sodium channels are essential in the generation and propagation of action potentials in neurons, translating into nerve impulse transmission. Abnormal sodium channel function is often a hallmark of pain disorders. Meanwhile, the **endocannabinoid system**—comprising **cannabinoid receptors**, **endogenous cannabinoids**, and **enzymes**—is known to regulate several physiological processes, including **pain modulation**. The connection between these two systems is still under investigation, but early studies indicate that cannabinoids can modulate sodium channel activity, pointing to potential analgesic properties.
Several cannabinoids, including **THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)** and **CBD (cannabidiol)**, have demonstrated varied interactions with sodium channels. THC is known for its psychoactive properties, which arise from its interaction with **CB1 receptors** in the brain, yet it also exhibits analgesic effects through less understood mechanisms. Conversely, CBD does not induce psychoactive effects and possesses anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties partly by acting on non-cannabinoid receptors, including sodium channels. Through these interactions, cannabinoids may dampen abnormal neuronal excitability associated with neuropathic pain, offering a multifaceted approach to pain management.
As we delve deeper into the molecular interactions between cannabinoids and sodium channels, the prospect of developing cannabinoid-based therapeutics for chronic pain conditions becomes increasingly viable. This blog provides a detailed overview of the underlying mechanisms and reviews pertinent studies that provide insights into this promising avenue for pain relief.
Features
Several professional and medical studies have shed light on how cannabinoids interact with sodium channels and their implications for analgesic effects. A study from the [Journal of Pain Research](https://www.dovepress.com/) highlights that cannabinoids can modulate **NaV1.7** sodium channels, which play a significant role in pain signalling pathways. This research underscores the potential for cannabinoids to reduce neuronal excitability, hence alleviating neuropathic pain conditions.
Another study featured in the [European Journal of Pharmacology](https://www.journals.elsevier.com/) explored how CBD affects sodium channel **isoforms** prevalent in peripheral pain pathways. The findings suggest that CBD exhibits a stabilizing effect on these channels, lessening hyperexcitability without inducing notable psychoactive effects, making it an attractive option for pain management.
Moreover, research published in the [Frontiers in Neurology](https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neurology) journal has shown that THC can selectively inhibit certain sodium channels, which may contribute to its analgesic properties in neuropathic pain. This action is hypothesized to occur via alteration in the biophysical properties of the channels, possibly providing both rapid and sustained pain relief.
Finally, a review in the [British Journal of Pharmacology](https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/) looked at the synergistic effects of cannabinoids, which might potentiate their ability to modulate sodium channel activity. The findings reflect on how different combinations of cannabinoids could enhance their efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, further supporting the pursuit of cannabinoid-based therapeutics.
Conclusion
The interactions between cannabinoids and sodium channels represent a promising frontier in the treatment of neuropathic pain. As scientific inquiry continues to elucidate these molecular mechanisms, the potential for cannabis-derived compounds to serve as effective and safer alternatives to traditional pain medications becomes increasingly tangible. With further research, cannabinoids could fundamentally transform chronic pain management, offering relief for those who suffer from debilitating neuropathic pain conditions. As always, continued studies will be essential in unlocking the full therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in this domain.
Concise Summary
The exploration of cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, highlights their promising potential for analgesic effects in neuropathic pain by interacting with sodium channels. Unlike traditional pain medications, cannabinoids offer a safer and more effective alternative. Research indicates they modulate sodium channels and reduce neuronal hyperexcitability. Studies suggest that CBD stabilizes sodium channels in peripheral pain pathways, and THC inhibits certain channels, contributing to pain relief. Further, combinations of cannabinoids might enhance efficacy, paving the way for cannabinoid-based therapeutics in chronic pain management. Continued research is essential to fully unlock their therapeutic potential.